Have you ever wondered why phase conductors in three phase power cables are continuously twisted around each other? The same concept why transposition in transmission line is done, which we will be discussing in this article.
What is Transposition
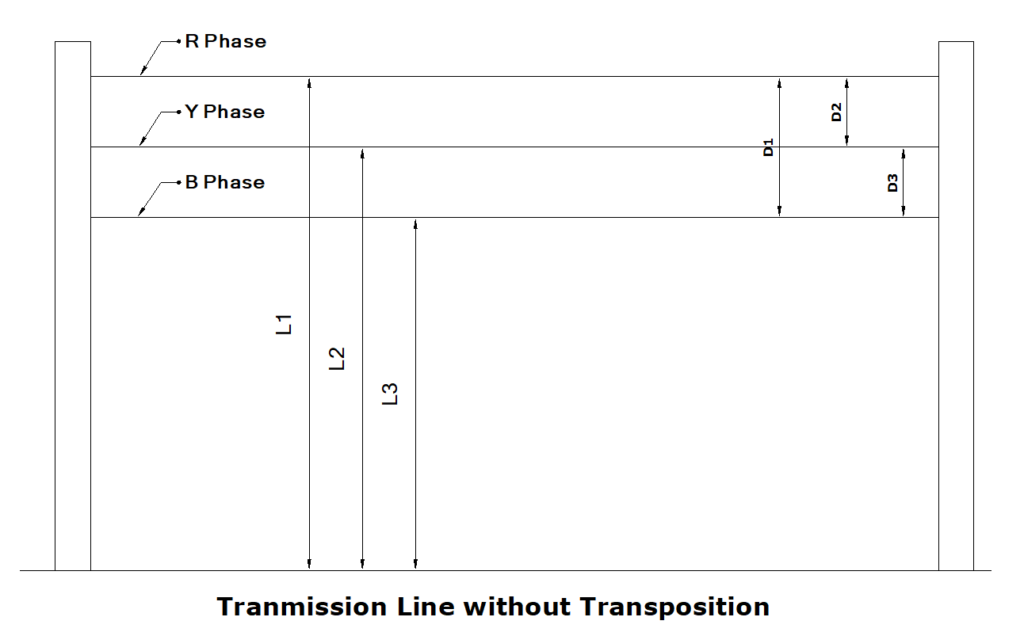
Assume a long distance power transmission line with no transposition employed. As it is a three phase power line, the sending end voltage for each phase will be same. But the distance between each phase conductor and ground will be different due to height difference. Due to that, line inductance and capacitance between each conductor and ground will not be the same. As a result, voltage drop in each phase will vary accordingly, and at the receiving end, there will be a major difference in the voltage of each phase.
In order to prevent that, Transposition of conductors is done at regular intervals. Transposition in transmission line is nothing but interchanging the positions of each phase conductor at regular intervals. By doing that, same average line inductance and capacitance for each phase will be achieved over entire length of the line.
How Transposition is Done
Transposition is done by specially designed transposition towers at regular intervals. These transposition towers contain special insulator arrangements and conductor shifting mechanisms. As shown in the diagram below, the position of each phase is interchanged such that each phase will be traveling in each position for equal distance.
The transposition of a transmission line follows a structured process:
Standard Transposition Cycle
A three-phase transmission line consists of three conductors: A, B, and C. Transposition is carried out in three segments:
- Segment 1: A → B → C
- Segment 2: B → C → A
- Segment 3: C → A → B
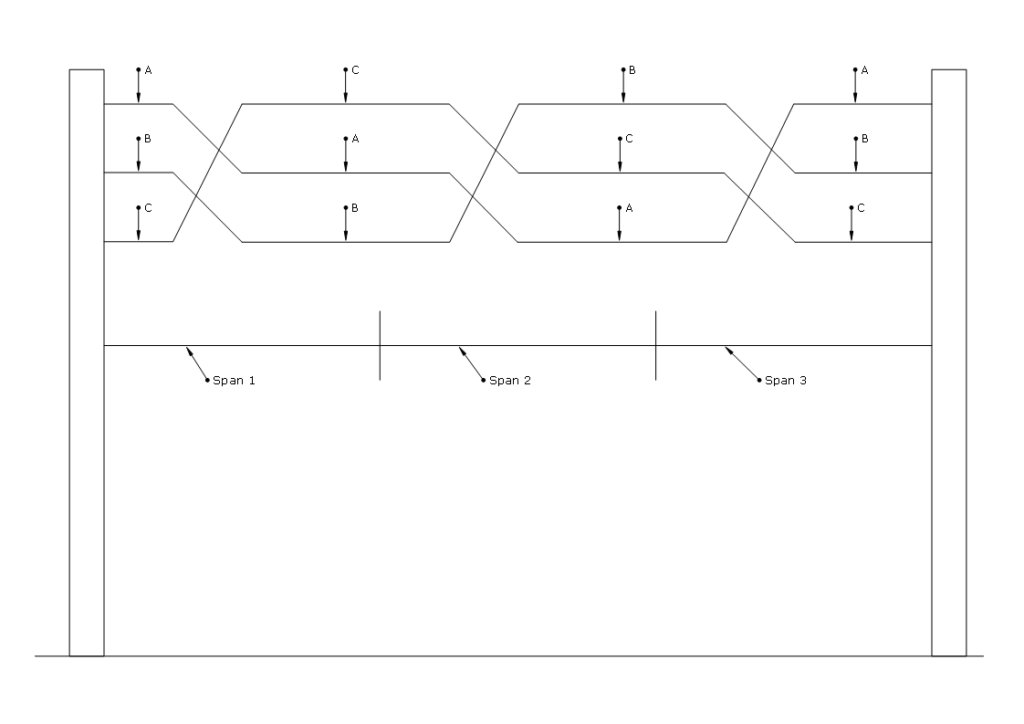
By the end of these three segments, each conductor has occupied all three positions, equalizing inductance and capacitance across the line.
Physical Implementation
- Transmission towers are designed to accommodate transposition points at regular intervals.
- Special insulator arrangements and conductor shifting mechanisms are used to facilitate smooth transposition.
Importance of Transposition
- Balancing Line Parameters: In an untransposed transmission line, each conductor have different distance from ground as well as each other, leading to variations in line inductance and capacitance of each phase.
- Reducing Electromagnetic Interference: Power lines generate electromagnetic fields (emf) which causes interference in nearby communication lines. Transposition distributes the emf evenly and reduces the interference.
- Improved Voltage Regulation: Unequal capacitance between each conductor causes voltage imbalances at the receiving end in case of long transmission lines. Transposition ensures uniform voltage distribution across all three phases.
Conclusion
Transposition in transmission lines play an important role in maintaining system efficiency, stability and reliability by balancing inductance and capacitance, reducing electromagnetic interference, and improving voltage regulation. It also requires complex transposition towers and special insulator arrangements to perform transposition. Hence it is usually planned for long distance transmission lines only.
Also Read : How Electricity Reaches Our Homes? A Simple Explanation from Power Generation to Utilization

